Invisible Battles: How AI Defends Against Its Own Kind
![]() Zsolt Vilhelm
Zsolt Vilhelm
![]() 2025.08.21
2025.08.21
Artificial intelligence has rapidly become an essential part of modern business operations, driving productivity and innovation across industries. Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) now power customer service chatbots, automate document processing, and even assist in software development. Yet the same technology that enables progress is also creating a new class of cyber threats, forcing organizations into a high-stakes battle of AI against AI.
Palo Alto Networks has launched three tools—AI Access Security, AI-SPM, and AI Runtime Security—built to tackle today’s AI-driven threats by detecting risks, blocking attacks, and safeguarding data from loss, tampering, or misuse.
The Rising Risks of AI Misuse
Attackers are already leveraging AI to enhance traditional cybercrime. Social engineering, once easy to spot through poor grammar or awkward phrasing, is now nearly undetectable as AI can generate flawless, tailored messages. Malicious “dark” LLMs such as WormGPT and Evil Bart are designed specifically to create harmful code, plan cyberattacks, and generate convincing phishing attempts.
Another emerging danger is prompt injection—manipulating an AI system’s input so it bypasses built-in security controls. This can result in the AI revealing restricted information, inserting false data, or performing harmful actions. The threat is no longer limited to text-based deception; these vulnerabilities can compromise complex AI-powered applications in real time.
Palo Alto Networks’ Three-Tiered Defense Strategy
1. AI Access Security
Monitors and identifies all AI usage within an organization, including unauthorized “shadow AI” tools. It categorizes AI applications (e.g., chatbots, code generators), blocks sensitive data such as personal IDs or credit card numbers from being transmitted, and applies policy-based controls to approve or restrict certain AI tools. This is not just a security measure—it also supports compliance with privacy laws and contractual data protection requirements.
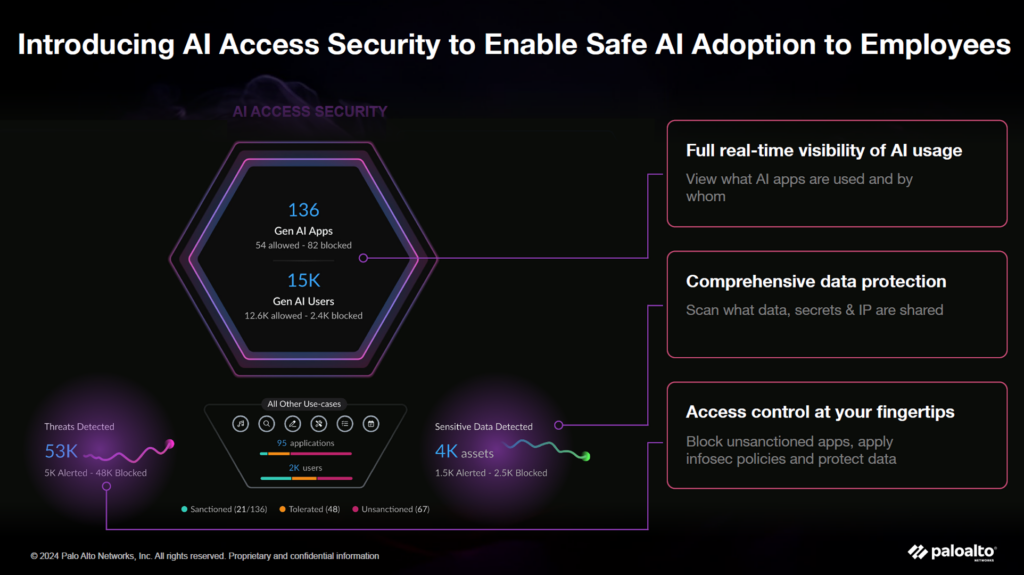
2. AI-SPM (Security Posture Management)
Offers a full security overview of an AI ecosystem, which can include GPUs, containers, databases, APIs, and third-party integrations. It inventories all system components, identifies vulnerabilities, maps how data flows between sources, and ranks risks so security teams can focus on the most urgent threats first. This is especially valuable for businesses that develop or customize AI tools.
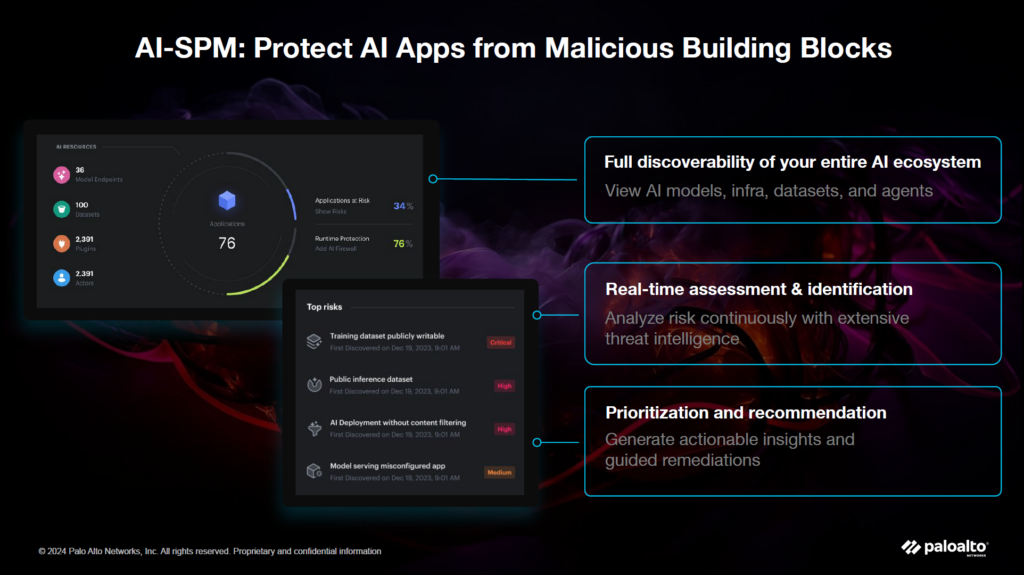
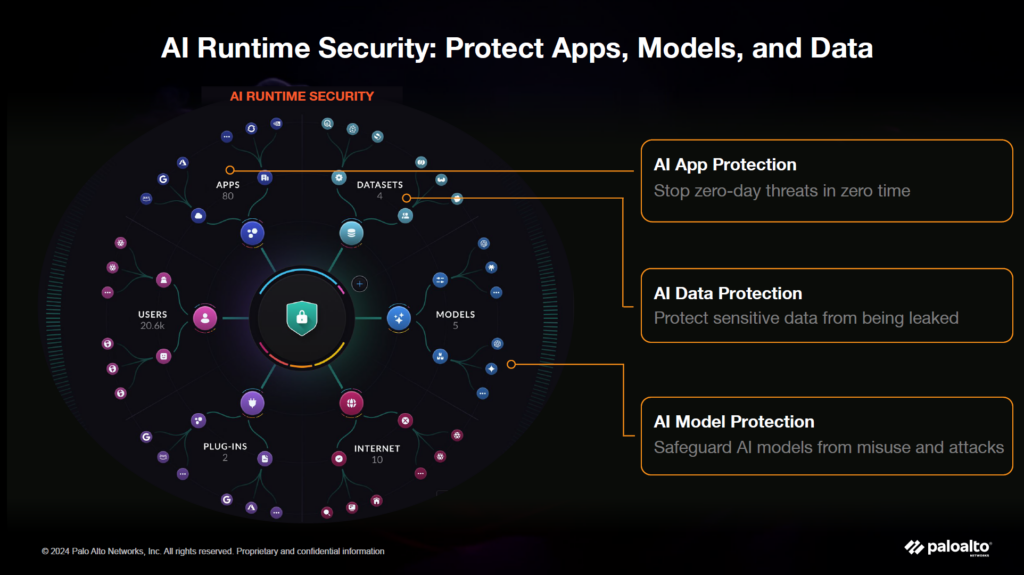
3. AI Runtime Security
Provides live protection for operational AI environments. It detects and blocks prompt injection attacks, scans AI outputs for poisoned data or malicious links, and controls network traffic between AI components, even in distributed cloud systems. This layer is critical for defending against attacks that occur after deployment, when systems are actively in use.
Addressing AI’s Top Security Challenges
With the launch of the LLM OWASP Top 10, the most common AI-specific vulnerabilities are now documented—prompt injection leads the list, followed by weaknesses in output handling and data access control. Palo Alto Networks’ solutions directly address several of these categories, shrinking the attack surface and strengthening overall resilience.
Securing the Future of AI
Adopting AI is no longer a competitive differentiator—it’s a basic requirement for staying relevant. But securing AI systems is just as essential as deploying them. Palo Alto Networks’ combined approach delivers visibility into AI usage, identifies and prioritizes vulnerabilities, and provides real-time defenses against malicious activity.
Artificial intelligence represents one of the greatest opportunities of the digital age—and one of its greatest risks. The key question is not whether organizations will use AI, but whether they can protect its value while defending against increasingly intelligent threats.
Read the full article on our International subsidiary’s website by clicking on the logo:


